ILSI entities around the world publish scientific articles on original research, literature reviews and gap analyses, as well as meeting proceedings in peer-reviewed journals and publications. Not one of the 1,000+ articles that ILSI has published over the last 45 years has ever been retracted. ILSI also publishes books, monographs, white papers, other scientific reports, annual reports and newsletters.
ILSI's flawless scientific publication track record, its commitment to the highest scientific standards and its adherence to rigorous scientific principles demonstrate its scientific integrity.
ILSI's publications are listed below by publication date, from the newest article to the oldest. You can also filter the list by title or publication type.
Publication Date
Journal Articles
An Algorithm to Assess Calcium Bioavailability from Foods
The Journal of Nutrition, 2023
- ILSI U.S. and Canada
Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 2023
- ILSI Europe
Obesity and excess adiposity are leading causes of metabolic and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Early identification of individuals at risk is key for preventive strategies. We examined the relationship between infant body composition (0–2 years of age) and later (>2 years) health outcomes using a systematic review.
15 anos da lei de biossegurança: o caso da soja GM no Brasil
2023
- ILSI Brasil
Bioactive compounds intake in the Brazilian population: Trends and determinants of socioeconomic inequalities between 2008 and 2018
PLOS ONE, 2023
- ILSI Brasil
Effect of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on Insulin Regulation, Glycemic Response, Appetite and Weight Management: A Systematic Review
Nutrition and Food Science, 2023
- ILSI-India
This is a systematic review on the effect of non-nutritive sweeteners on appetite, weight, glycemic regulation, and gut microbiome.
WP_Query Object
(
[query] => Array
(
[post_type] => publication
[posts_per_page] => 5
[type] =>
[area] =>
[committee] =>
[authors] =>
[showtitle] =>
[meta_query] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_type
[value] => journal-article
[compare] => =
)
)
[tax_query] => Array
(
)
[paged] => 2
[meta_key] => _ilsi_date
[orderby] => meta_value
[order] => DESC
)
[query_vars] => Array
(
[post_type] => publication
[posts_per_page] => 5
[type] =>
[area] =>
[committee] =>
[authors] =>
[showtitle] =>
[meta_query] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_type
[value] => journal-article
[compare] => =
)
)
[tax_query] => Array
(
)
[paged] => 2
[meta_key] => _ilsi_date
[orderby] => meta_value
[order] => DESC
[error] =>
[m] =>
[p] => 0
[post_parent] =>
[subpost] =>
[subpost_id] =>
[attachment] =>
[attachment_id] => 0
[name] =>
[pagename] =>
[page_id] => 0
[second] =>
[minute] =>
[hour] =>
[day] => 0
[monthnum] => 0
[year] => 0
[w] => 0
[category_name] =>
[tag] =>
[cat] =>
[tag_id] =>
[author] =>
[author_name] =>
[feed] =>
[tb] =>
[meta_value] =>
[preview] =>
[s] =>
[sentence] =>
[title] =>
[fields] =>
[menu_order] =>
=>
[category__in] => Array
(
)
[category__not_in] => Array
(
)
[category__and] => Array
(
)
[post__in] => Array
(
)
[post__not_in] => Array
(
)
[post_name__in] => Array
(
)
[tag__in] => Array
(
)
[tag__not_in] => Array
(
)
[tag__and] => Array
(
)
[tag_slug__in] => Array
(
)
[tag_slug__and] => Array
(
)
[post_parent__in] => Array
(
)
[post_parent__not_in] => Array
(
)
[author__in] => Array
(
)
[author__not_in] => Array
(
)
[search_columns] => Array
(
)
[ignore_sticky_posts] =>
[suppress_filters] =>
[cache_results] => 1
[update_post_term_cache] => 1
[update_menu_item_cache] =>
[lazy_load_term_meta] => 1
[update_post_meta_cache] => 1
[nopaging] =>
[comments_per_page] => 50
[no_found_rows] =>
)
[tax_query] => WP_Tax_Query Object
(
[queries] => Array
(
)
[relation] => AND
[table_aliases:protected] => Array
(
)
[queried_terms] => Array
(
)
[primary_table] => wp_posts
[primary_id_column] => ID
)
[meta_query] => WP_Meta_Query Object
(
[queries] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_date
)
[1] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_type
[value] => journal-article
[compare] => =
)
[relation] => OR
)
[relation] => AND
)
[relation] => AND
[meta_table] => wp_postmeta
[meta_id_column] => post_id
[primary_table] => wp_posts
[primary_id_column] => ID
[table_aliases:protected] => Array
(
[0] => wp_postmeta
[1] => mt1
)
[clauses:protected] => Array
(
[wp_postmeta] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_date
[compare] => =
[compare_key] => =
[alias] => wp_postmeta
[cast] => CHAR
)
[mt1] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_type
[value] => journal-article
[compare] => =
[compare_key] => =
[alias] => mt1
[cast] => CHAR
)
)
[has_or_relation:protected] =>
)
[date_query] =>
[request] =>
SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS wp_posts.ID
FROM wp_posts INNER JOIN wp_postmeta ON ( wp_posts.ID = wp_postmeta.post_id ) INNER JOIN wp_postmeta AS mt1 ON ( wp_posts.ID = mt1.post_id )
WHERE 1=1 AND (
wp_postmeta.meta_key = '_ilsi_date'
AND
(
( mt1.meta_key = '_ilsi_type' AND mt1.meta_value = 'journal-article' )
)
) AND ((wp_posts.post_type = 'publication' AND (wp_posts.post_status = 'publish' OR wp_posts.post_status = 'acf-disabled')))
GROUP BY wp_posts.ID
ORDER BY wp_postmeta.meta_value DESC
LIMIT 5, 5
[posts] => Array
(
[0] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 40093
[post_author] => 342
[post_date] => 2024-02-08 16:33:01
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-02-08 21:33:01
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => An Algorithm to Assess Calcium Bioavailability from Foods
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => an-algorithm-to-assess-calcium-bioavailability-from-foods
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-02-08 16:44:45
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-02-08 21:44:45
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/?post_type=publication&p=40093
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[1] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 39110
[post_author] => 351
[post_date] => 2023-11-09 08:52:48
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-11-09 08:52:48
[post_content] =>
Objective
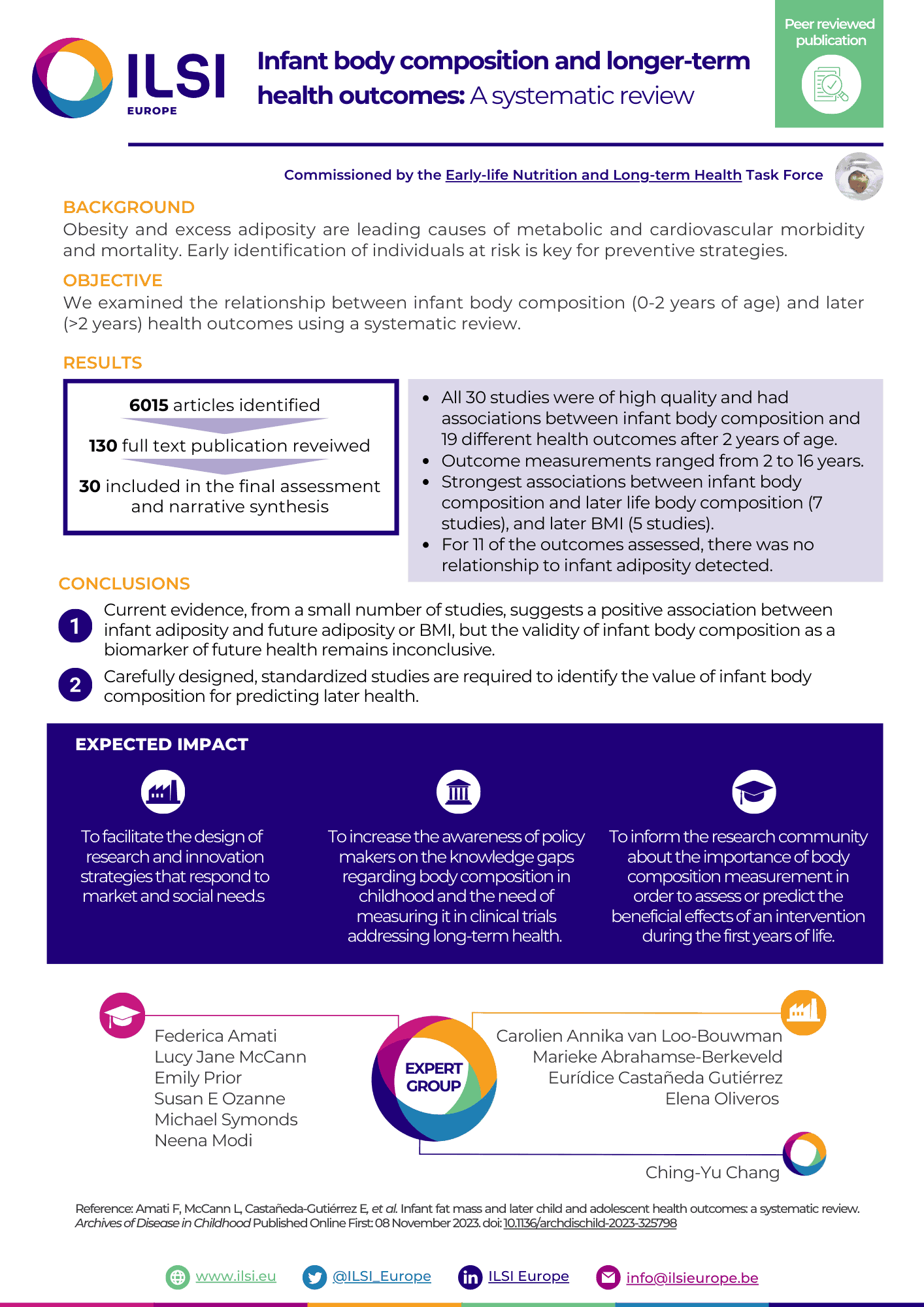
Obesity and excess adiposity are leading causes of metabolic and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Early identification of individuals at risk is key for preventive strategies. We examined the relationship between infant body composition (0-2 years of age) and later (>2 years) health outcomes using a systematic review.
Design
We preregistered the study on PROSPERO (ID 288013) and searched Embase, PubMed and Cochrane databases for English language publications using the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms 'infant' and 'body composition' and 'risk' between January 1946 and February 2022. We included studies which assessed infant body composition using predetermined in vivo methods other than body mass index (BMI).
Results
We identified 6015 articles. After abstract screening to assess eligibility, we reviewed 130 full text publications. 30 were included in the final assessment and narrative synthesis. Meta-analysis was not possible due to heterogeneity of results. All 30 studies were of high quality and reported associations between infant body composition and 19 different health outcomes after 2 years of age. Outcome measurements ranged from 2 years to 16 years. The strongest associations were found between infant fat mass and later fat mass (7 studies), and later BMI (5 studies). For 11 of the outcomes assessed, there was no relationship to infant adiposity detected.
Conclusions
Current evidence, from a small number of studies, suggests a positive association between infant adiposity and future adiposity or BMI, but the validity of infant body composition as a biomarker of future health remains inconclusive. Carefully designed, standardised studies are required to identify the value of infant body composition for predicting later health.
Download the full article here.
Download the article one-pager below
 [post_title] => Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-03-15 11:13:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[2] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38759
[post_author] => 40
[post_date] => 2023-10-05 16:56:40
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-05 21:56:40
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => 15 anos da lei de biossegurança: o caso da soja GM no Brasil
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => 15-anos-da-lei-de-biosseguranca-o-caso-da-soja-gm-no-brasil
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-12-08 13:07:17
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-12-08 18:07:17
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/15-anos-da-lei-de-biosseguranca-o-caso-da-soja-gm-no-brasil/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[3] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38953
[post_author] => 40
[post_date] => 2023-10-17 11:46:31
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-17 15:46:31
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Bioactive compounds intake in the Brazilian population: Trends and determinants of socioeconomic inequalities between 2008 and 2018
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => bioactive-compounds-intake-in-the-brazilian-population-trends-and-determinants-of-socioeconomic-inequalities-between-2008-and-2018
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-10-17 11:52:52
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-10-17 15:52:52
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/bioactive-compounds-intake-in-the-brazilian-population-trends-and-determinants-of-socioeconomic-inequalities-between-2008-and-2018/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[4] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38745
[post_author] => 357
[post_date] => 2023-10-04 03:08:55
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-04 07:08:55
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Effect of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on Insulin Regulation, Glycemic Response, Appetite and Weight Management: A Systematic Review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => effect-of-non-nutritive-sweeteners-on-insulin-regulation-glycemic-response-appetite-and-weight-management-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-10-04 03:08:55
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-10-04 07:08:55
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/effect-of-non-nutritive-sweeteners-on-insulin-regulation-glycemic-response-appetite-and-weight-management-a-systematic-review/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
)
[post_count] => 5
[current_post] => -1
[before_loop] =>
[in_the_loop] =>
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 40093
[post_author] => 342
[post_date] => 2024-02-08 16:33:01
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-02-08 21:33:01
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => An Algorithm to Assess Calcium Bioavailability from Foods
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => an-algorithm-to-assess-calcium-bioavailability-from-foods
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-02-08 16:44:45
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-02-08 21:44:45
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/?post_type=publication&p=40093
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[comment_count] => 0
[current_comment] => -1
[found_posts] => 556
[max_num_pages] => 112
[max_num_comment_pages] => 0
[is_single] =>
[is_preview] =>
[is_page] =>
[is_archive] =>
[is_date] =>
[is_year] =>
[is_month] =>
[is_day] =>
[is_time] =>
[is_author] =>
[is_category] =>
[is_tag] =>
[is_tax] =>
[is_search] =>
[is_feed] =>
[is_comment_feed] =>
[is_trackback] =>
[is_home] => 1
[is_privacy_policy] =>
[is_404] =>
[is_embed] =>
[is_paged] => 1
[is_admin] =>
[is_attachment] =>
[is_singular] =>
[is_robots] =>
[is_favicon] =>
[is_posts_page] =>
[is_post_type_archive] =>
[query_vars_hash:WP_Query:private] => 3e93003149149963e9e0acd69db53ac4
[query_vars_changed:WP_Query:private] =>
[thumbnails_cached] =>
[allow_query_attachment_by_filename:protected] =>
[stopwords:WP_Query:private] =>
[compat_fields:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => query_vars_hash
[1] => query_vars_changed
)
[compat_methods:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => init_query_flags
[1] => parse_tax_query
)
)
[post_title] => Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-03-15 11:13:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[2] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38759
[post_author] => 40
[post_date] => 2023-10-05 16:56:40
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-05 21:56:40
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => 15 anos da lei de biossegurança: o caso da soja GM no Brasil
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => 15-anos-da-lei-de-biosseguranca-o-caso-da-soja-gm-no-brasil
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-12-08 13:07:17
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-12-08 18:07:17
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/15-anos-da-lei-de-biosseguranca-o-caso-da-soja-gm-no-brasil/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[3] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38953
[post_author] => 40
[post_date] => 2023-10-17 11:46:31
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-17 15:46:31
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Bioactive compounds intake in the Brazilian population: Trends and determinants of socioeconomic inequalities between 2008 and 2018
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => bioactive-compounds-intake-in-the-brazilian-population-trends-and-determinants-of-socioeconomic-inequalities-between-2008-and-2018
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-10-17 11:52:52
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-10-17 15:52:52
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/bioactive-compounds-intake-in-the-brazilian-population-trends-and-determinants-of-socioeconomic-inequalities-between-2008-and-2018/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[4] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38745
[post_author] => 357
[post_date] => 2023-10-04 03:08:55
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-04 07:08:55
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Effect of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on Insulin Regulation, Glycemic Response, Appetite and Weight Management: A Systematic Review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => effect-of-non-nutritive-sweeteners-on-insulin-regulation-glycemic-response-appetite-and-weight-management-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-10-04 03:08:55
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-10-04 07:08:55
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/publication/effect-of-non-nutritive-sweeteners-on-insulin-regulation-glycemic-response-appetite-and-weight-management-a-systematic-review/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
)
[post_count] => 5
[current_post] => -1
[before_loop] =>
[in_the_loop] =>
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 40093
[post_author] => 342
[post_date] => 2024-02-08 16:33:01
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-02-08 21:33:01
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => An Algorithm to Assess Calcium Bioavailability from Foods
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => an-algorithm-to-assess-calcium-bioavailability-from-foods
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-02-08 16:44:45
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-02-08 21:44:45
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.org/?post_type=publication&p=40093
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[comment_count] => 0
[current_comment] => -1
[found_posts] => 556
[max_num_pages] => 112
[max_num_comment_pages] => 0
[is_single] =>
[is_preview] =>
[is_page] =>
[is_archive] =>
[is_date] =>
[is_year] =>
[is_month] =>
[is_day] =>
[is_time] =>
[is_author] =>
[is_category] =>
[is_tag] =>
[is_tax] =>
[is_search] =>
[is_feed] =>
[is_comment_feed] =>
[is_trackback] =>
[is_home] => 1
[is_privacy_policy] =>
[is_404] =>
[is_embed] =>
[is_paged] => 1
[is_admin] =>
[is_attachment] =>
[is_singular] =>
[is_robots] =>
[is_favicon] =>
[is_posts_page] =>
[is_post_type_archive] =>
[query_vars_hash:WP_Query:private] => 3e93003149149963e9e0acd69db53ac4
[query_vars_changed:WP_Query:private] =>
[thumbnails_cached] =>
[allow_query_attachment_by_filename:protected] =>
[stopwords:WP_Query:private] =>
[compat_fields:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => query_vars_hash
[1] => query_vars_changed
)
[compat_methods:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => init_query_flags
[1] => parse_tax_query
)
)